Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
02. Planar field mapping#
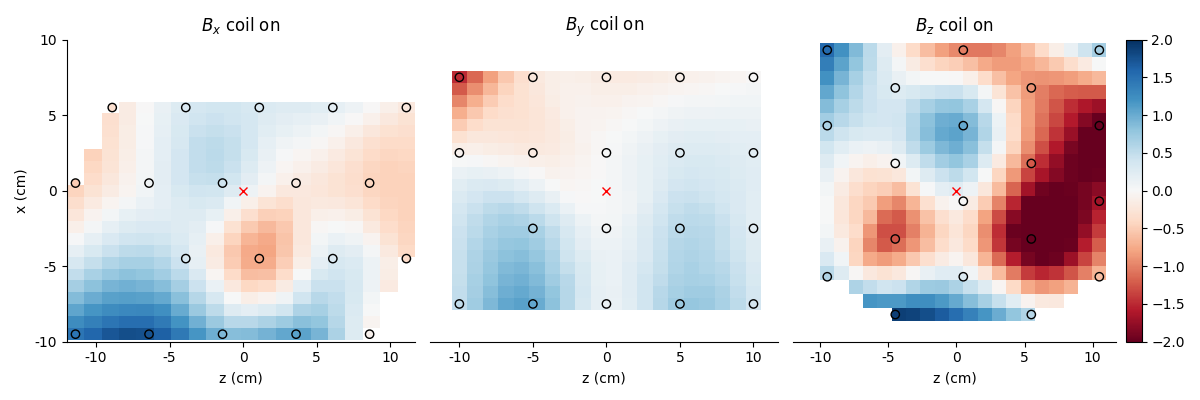
Example demonstrating how to map the background field along a plane.
# Authors: Mainak Jas <mjas@mgh.harvard.edu>
# Padma Sundaram <padma@nmr.mgh.harvard.edu>
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import FormatStrFormatter
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
from scipy.interpolate import griddata
from opmcoils.analysis import load_remnant_fields
First, we define the coordinates of the sensors from the 3D model of the sensor holders.
def get_coords(component):
if component == 'y':
x = [0, 5, 10, 15, 20,
0, 5, 10, 15, 20,
5, 10, 15, 20,
0, 5, 10, 15, 20]
z = [15, 15, 15, 15, 15,
10, 10, 10, 10, 10,
5, 5, 5, 5,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
x = np.array(x) - 10
z = np.array(z) - 7.5
txt_fname = 'fine_zero_y.txt'
if component == 'z':
z = [17.5, 15, 17.5, 15, 17.5,
12.5, 10, 12.5, 10, 12.5,
5, 7.5, 5, 7.5,
2.5, 0, 2.5, 0, 2.5]
x = [0, 5, 10, 15, 20,
0, 5, 10, 15, 20,
5, 10, 15, 20,
0, 5, 10, 15, 20]
x = np.array(x) - 9.5
z = np.array(z) - 8.2
txt_fname = 'fine_zero_z.txt'
elif component == 'x':
x = [2.5, 7.5, 12.5, 17.5, 22.5,
0, 5, 10, 15, 20,
7.5, 12.5, 17.5, 22.5,
0, 5, 10, 15, 20]
z = [15, 15, 15, 15, 15,
10, 10, 10, 10, 10,
5, 5, 5, 5,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
x = np.array(x) - 11.4
z = np.array(z) - 9.5
txt_fname = 'fine_zero_x.txt'
return x, z, txt_fname
The bias for each sensor is predefined in a dictionary.
folder = Path.cwd() / 'data'
bias = {'00:01': -0.06, '00:03': -0.74, '00:04': 0.51, '00:08': -0.43,
'00:11': 0.11, '00:14': -0.13, '00:07': -0.42, '00:15': 1.23,
'00:16': 0.07, '01:01': 0.42, '01:03': 0.19, '01:04': 0.02,
'01:06': 0.22, '01:08': -0.33, '01:09': 0.30,
'01:10': -0.12, '01:13': -1.95, '01:14': 0.65, '01:15': 0.27,
'01:16': 0.62}
ch_names = ['01:16', '01:13', '00:04', '01:01', '01:08',
'01:10', '01:09', '01:03', '00:16', '01:04',
'00:08', '00:15', '00:03', '00:11',
'01:15', '00:01', '01:06', '00:14', '01:14']
Finally, we plot the field along the x-z plane.
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(12, 4), sharex=True, sharey=True)
for ax, component in zip(axes, ['x', 'y', 'z']):
x, z, txt_fname = get_coords(component)
B = load_remnant_fields(f'{folder}/{txt_fname}',
ch_names=ch_names, bias=bias)
xi = np.linspace(np.min(x), np.max(x), 20)
zi = np.linspace(np.min(z), np.max(z), 20)
Xi, Zi = np.meshgrid(xi, zi)
Bi = griddata((x, z), B, (Xi, Zi), method='cubic')
vmin, vmax = -2, 2
im = ax.pcolormesh(Xi, Zi, Bi, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, cmap='RdBu')
if component == 'z':
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
cax = divider.append_axes('right', size='5%', pad=0.1)
cbar = fig.colorbar(im, cax=cax)
ax.scatter(x, z, c=B, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax,
edgecolors='k', cmap='RdBu')
ax.plot(0, 0, 'rx')
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%d'))
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%d'))
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.set_yticks(np.linspace(-10, 10, 5))
if component != 'x':
ax.spines['left'].set_visible(False)
ax.tick_params(axis='y', which='both', left=False)
ax.set_xticks(np.linspace(-10, 10, 5))
ax.set_xlabel('z (cm)')
ax.set_title(f'$B_{component}$ coil on')
axes[0].set_ylabel('x (cm)')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.118 seconds)